Table of Contents
ToggleCatalog numbers are important when dealing with circuit breakers as they help you select the correct breaker for your specific application. In this case, we’re focusing on the F Frame circuit breakers, which typically have a range of amperage ratings from 15 to 100 amps. Let’s explore the importance of catalog numbers and how they impact your choice of circuit breaker.
Locating the Catalog Number
To find the catalog number on your circuit breaker, simply look to the left of the operator switch. You’ll first see the amperage rating, followed by the catalog number. For example, the catalog number “FAL36020” corresponds to a specific F Frame circuit breaker.
Here’s an example of where to look to find the catalog number:
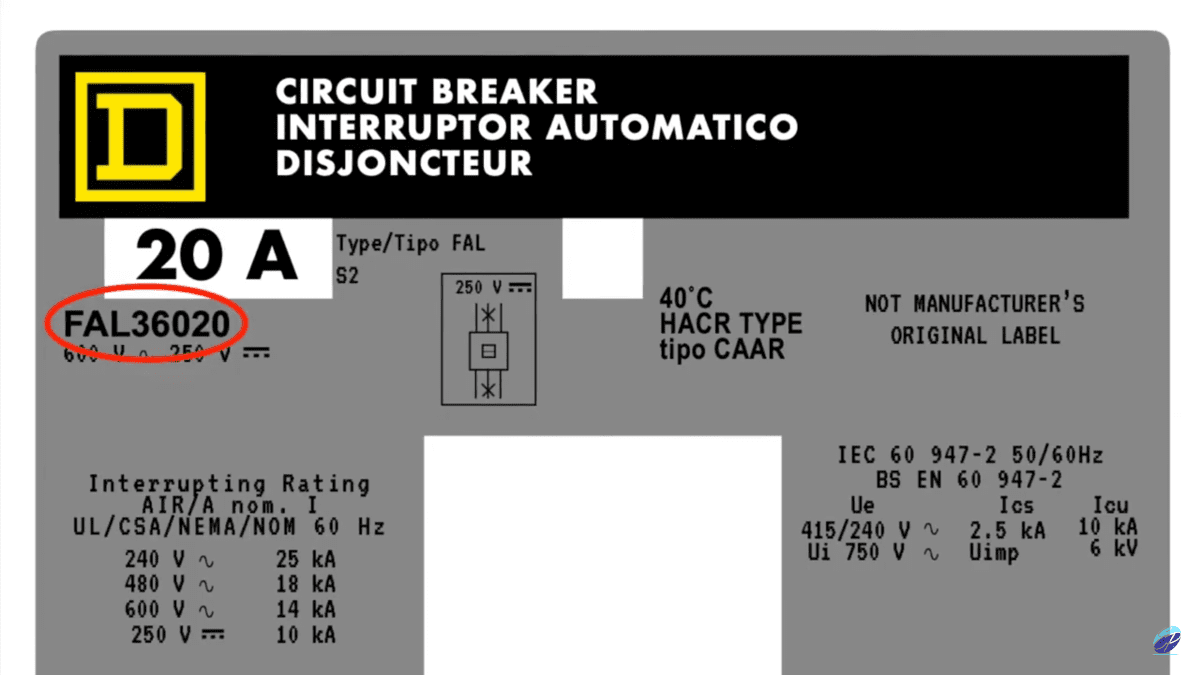
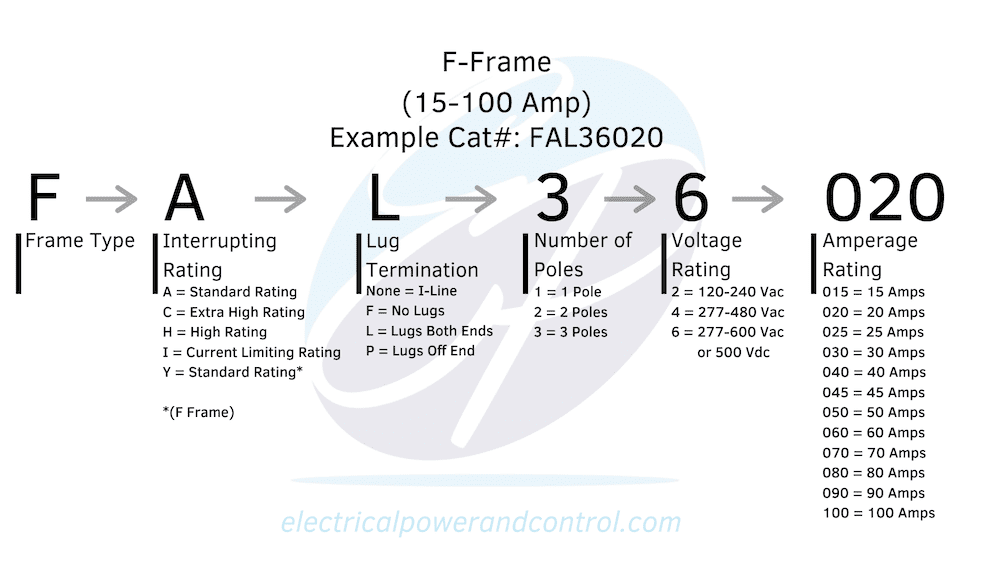
Breaking Down the Catalog Number
Each character in the catalog number has a specific meaning and impact on the type of circuit breaker you need:
- First character: Refers to the frame type (F in this case) and how it will fit into your application.
- Second character: Indicates the interrupting capacity, which is the maximum interrupting capacity of the circuit breaker. For example, if this digit was a “C”, it would denote an extra-high interrupting capacity, making it an “FC”.
- Third character: Refers to the lug configuration, determining whether there are lugs on one end, both ends, or no lugs at all, depending on your specific application.
- Fourth character: Represents the number of poles on the circuit breaker, which can be one, two, or three poles, as indicated by the digits “1”, “2”, or “3”, respectively.
- Fifth character: Indicates the voltage class of the circuit breaker. For instance, a “6” denotes 600 volts, a “4” represents 480 volts, and a “2” stands for 240 volts.
- Sixth, seventh, and eighth character: This three-digit number specifies the amperage rating of the frame, which is crucial for selecting the right circuit breaker. In our example, the “020” indicates a 20-amp circuit breaker.
By understanding the significance of each character in the catalog number, you can confidently select the appropriate circuit breaker for your application. This ensures safety, compatibility, and optimal performance in your electrical system.
Now, let’s go into more detail about the catalog number and what each character represents. This understanding will empower you to make informed choices when selecting a circuit breaker for your unique requirements.



Frame Type
The first character of the catalog number relates to the frame type, which, in this instance, is denoted by the letter “F.” This frame type is essential because it dictates how the breaker will physically fit into your application. Different frame types have distinct dimensions and mounting configurations, so ensuring you select the correct frame is crucial for compatibility and performance.
The frame of an industrial circuit breaker is essentially the structural component that houses the internal parts of the breaker, including the operating mechanism, contacts, and the arc extinguishing system. It provides mechanical support and protection, ensuring that the breaker can withstand physical stresses and environmental conditions it may encounter in industrial settings.
Interrupting Capacity
Moving on to the second character, we find information about the maximum interrupting capacity of the circuit breaker. In our example catalog number “FAL36020,” the “A” indicates a standard interrupting capacity level. Other letters indicate different interrupting capacity levels:
- A = Standard
- C = Extra High
- H = High
- I = Current Limiting
The interrupting capacity is a critical specification as it determines the breaker’s ability to handle electrical faults and protect your equipment. Choosing a breaker with the right interrupting capacity ensures that it can effectively manage the amount of current flowing through your electrical system during abnormal conditions.
Lug Configuration
The third character of the catalog number addresses the lug configuration, offering flexibility in how the breaker connects to your application. Different lug configurations include lugs on one end, both ends, or no lugs at all. This variation allows for customization based on your specific installation requirements.
- F = No Lugs
- L = Both Ends
- P = One End
The lug configuration is an important consideration as it influences the ease and adaptability of connecting your circuit breaker to the rest of your electrical system. It ensures that you can securely and appropriately integrate the breaker into your setup.
Number of Poles
The fourth character in the catalog number is designated to indicate the number of poles. This character can typically be a number ranging from 1 to 3, reflecting the configuration of the breaker. Here’s what these numbers generally represent:
- Single-pole = suitable for protecting one circuit
- Double-pole = used for controlling two circuits or a 240-volt circuit
- Three-pole = commonly used in three-phase systems
Poles refer to the number of circuits the breaker can protect. Each pole acts as a separate circuit protector, enabling individual control and protection mechanisms for each connected circuit. This modular approach allows for the safeguarding of the electrical system, ensuring that an issue in one circuit does not impact the others.
Circuit breaker poles are integral to maintaining the safety and operational integrity of electrical installations. They prevent overcurrent, which can lead to overheating, damage to equipment, or even fire, by interrupting the flow of electrical current.
Voltage Class
The fifth character in the catalog number indicates the voltage class. This is a critical characteristic as it defines the maximum voltage the circuit breaker can handle effectively. The voltage class is represented by a number; each number corresponds to a particular voltage level. Common examples of these numerical indicators include:
- 2 = 240V
- 4 = 480V
- 6 = 600V
It’s important to note that these are for the F frame we’re using as an example and manufacturers might have additional codes for other specific voltage classes or variations within these broad categories.
Frame Amperage
The last three characters of the catalog number tell you the amperage rating of the frame, which indicates the maximum current the breaker can safely carry without tripping. These characters will be a three-digit number that gives you immediate insight into the device’s capacity.
These numbers can vary, but in “F” frame type breakers from 15-100 amps, the numbers might be:
- 015 for 15 amps
- 020 for 20 amps
- 030 for 30 amps
- 100 for 100 amps
Understanding the amperage rating of a circuit breaker is crucial for several reasons. Primarily, it ensures that the breaker can handle the maximum expected current load without tripping under normal conditions. This is essential for maintaining both safety and efficiency in electrical systems.
A breaker with too low an amperage rating for the circuit it protects could trip frequently, causing unnecessary downtime and potential safety hazards. Conversely, a breaker rated too high may not protect the circuit adequately, leading to possible overloads and even fires.
Configuration Charts for Frame Breaker Types
To make selecting the right circuit breaker even easier, we’ve created comprehensive charts that break down the different configurations available. These charts are designed to enhance your understanding and enable quick decision-making when choosing a breaker.
Above is the chart for 15 to 100 amp F frame breakers, but below you can view and save charts for other frame types including M, L, and K frame breakers from Square D:
These charts offer a visual representation of the different configurations available, making it easier to compare. They show possible combinations of interrupting capacities, lug configurations, pole counts, voltage classes, and amperage ratings for the specific frame types.
This allows you to quickly identify the breakers that meet your specific requirements.
Selecting Your Circuit Breaker
Now that you understand the significance of each character in the catalog number and are armed with charts, it’s time to dive into the process of selecting the right circuit breaker for your unique needs.
Steps to Identifying Your Requirements
Before making your selection, it’s crucial to identify your specific requirements. Ask yourself the following questions:
- What are the physical dimensions and mounting configuration needed for my application?
- What interrupting capacity do I require to handle electrical faults effectively?
- Which lug configuration best suits my installation needs?
- How many poles does my circuit breaker need to have?
- What voltage class and amperage rating are compatible with my electrical system?
By answering these questions, you can narrow down your options and choose a circuit breaker that aligns perfectly with your application.
Best Practices for Selection
When selecting a circuit breaker, it’s essential to consider best practices to ensure optimal performance and safety. Here are some key practices to keep in mind:
- Identify the specific needs of your electrical system. Consider factors such as the voltage, amperage, and types of equipment being used.
- Determine the environment: The location (indoor, outdoor, corrosive environment) will influence your choice.
- Consider scalability: If you anticipate future expansion or changes in your electrical system, choose breakers that can accommodate growth.
- Mounting configuration: Select a breaker with a mounting configuration that fits your panelboard or enclosure.
- Seek expert advice: A licensed technician can assess your specific requirements and provide personalized recommendations.
By following these best practices, you can be confident in your selection and maximize the performance and longevity of your circuit breaker.
Mastering Circuit Breaker Selection
Understanding circuit breaker catalog numbers doesn’t have to be complicated. With a little knowledge, you can make informed choices that ensure the safety and efficiency of your electrical system.
Remember, the catalog number provides essential information about the breaker’s frame type, interrupting capacity, lug configuration, number of poles, voltage class, and amperage rating. By carefully considering these, you’ll be able to select the perfect breaker for your application.
Need expert guidance? Electrical Power and Control is here to help! Our team of professionals is ready to provide personalized advice and ensure you choose the right circuit breaker for your specific needs.
So, don’t hesitate to reach out! Give us a call at (205) 812-5402 and let us assist you in making informed decisions that will benefit your electrical system for years to come.