Table of Contents
ToggleElectrical enclosures are protective housings designed to safeguard electrical components such as circuit breakers, switches, and control panels. They serve a dual purpose: protecting the internal components from environmental factors like dust, moisture, and accidental contact, and ensuring the safety of personnel by preventing exposure to live parts .
In industrial and commercial settings, electrical enclosures are indispensable. They shield sensitive equipment from harsh conditions, mechanical impacts, and unauthorized access, thereby reducing the risk of malfunctions and safety hazards .
This article explores the various types of electrical enclosures, their benefits, industry applications, and key considerations for selecting the right enclosure to meet specific operational needs.
What Are Electrical Enclosures?
Electrical enclosures are protective housings designed to safeguard electrical or electronic equipment, such as circuit breakers, switches, and control panels. They serve a dual purpose: protecting the internal components from environmental factors like dust, moisture, and accidental contact, and ensuring the safety of personnel by preventing exposure to live parts .
These enclosures are essential in various settings, from industrial facilities to commercial buildings, where they help maintain the integrity and reliability of electrical systems. By providing a controlled environment, electrical enclosures contribute to the longevity of equipment and reduce the risk of electrical hazards .
Selecting the appropriate enclosure involves considering factors such as the operating environment, the type of equipment housed, and compliance with relevant standards like NEMA or IP ratings. Proper selection ensures optimal protection and performance of electrical systems.
Common Types of Electrical Enclosures
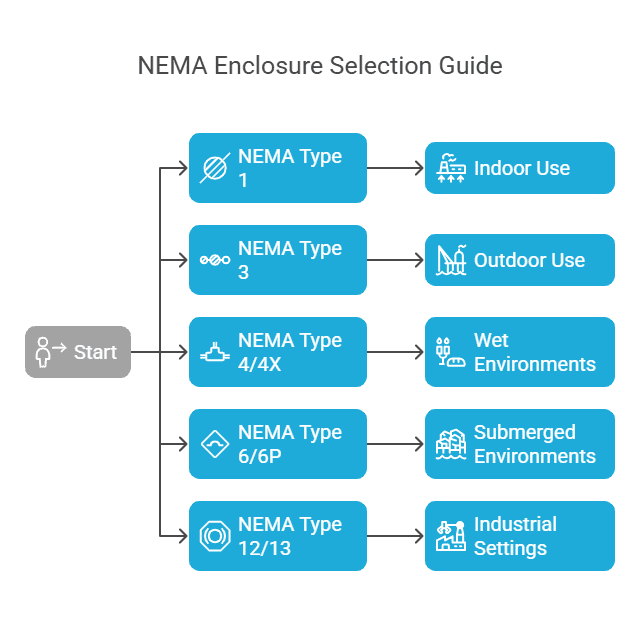
Electrical enclosures are designed to protect electrical components from environmental hazards and unauthorized access. The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) classifies these enclosures into various types, each suited for specific conditions and applications. Understanding these classifications helps in selecting the appropriate enclosure for your needs.
NEMA Type 1: General-Purpose Indoor Enclosures
- Protection Level: Provides a basic level of protection against dust and light, indirect contact with electrical equipment.
- Applications: Suitable for indoor use in environments like offices and light industrial settings where minimal environmental hazards exist.
- Limitations: Not designed to protect against water ingress or corrosive substances.
NEMA Type 3: Weather-Resistant Outdoor Enclosures
- Protection Level: Offers protection against falling dirt, windblown dust, rain, sleet, and snow.
- Applications: Ideal for outdoor use on ship docks, construction sites, and tunnels.
- Special Features: Constructed to remain undamaged by the formation of ice on the enclosure.
NEMA Type 4 and 4X: Watertight and Corrosion-Resistant Enclosures
- Protection Level: Protects against windblown dust and rain, splashing water, and hose-directed water.
- Applications: Suitable for indoor or outdoor use in dairies, breweries, and wastewater treatment plants.
- Type 4X: Provides an additional level of protection against corrosion, making it ideal for marine environments.
NEMA Type 6 and 6P: Submersible Enclosures
- Protection Level: Designed to protect against the ingress of water during occasional temporary submersion at limited depths (Type 6) and prolonged submersion (Type 6P).
- Applications: Used in quarries, mines, and manholes where equipment may be exposed to water submersion.
- Type 6P: Offers an additional level of protection against corrosion.
NEMA Type 12 and 13: Dust-Tight Enclosures for Industrial Use
- Protection Level: Provides protection against dust, falling dirt, and dripping non-corrosive liquids.
- Applications: Commonly used in industrial settings such as manufacturing plants and warehouses.
- Type 13: Also offers protection against the spraying and seepage of oil and non-corrosive coolants.
NEMA and IP Ratings Explained
When selecting an electrical enclosure, understanding its protective capabilities is crucial. Two primary standards define these protections: the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) ratings and the Ingress Protection (IP) ratings.
What is a NEMA Rating?
NEMA ratings, established by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association, classify enclosures based on their ability to withstand environmental conditions. These ratings consider factors like protection against dust, water, corrosion, and other hazards. For instance, a NEMA 4X enclosure offers protection against corrosion, windblown dust, rain, splashing water, and hose-directed water, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor use.
What is an IP Rating?
The IP rating system, defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) under standard IEC 60529, indicates the degree of protection an enclosure provides against the intrusion of solid objects and liquids. An IP rating consists of two digits: the first denotes protection against solids (like dust), and the second against liquids (like water). For example, an IP66 rating means the enclosure is dust-tight and protected against powerful water jets.
Why Ratings Matter in Selecting an Enclosure
Choosing the correct enclosure rating ensures the safety and longevity of electrical components. An enclosure with an inadequate rating may fail under specific environmental conditions, leading to equipment damage or safety hazards. Understanding these ratings helps in selecting enclosures that match the operational environment’s demands.
NEMA vs. IP Ratings: A Comparison
While both NEMA and IP ratings serve to classify enclosure protections, they differ in scope and application. NEMA ratings are predominantly used in North America and encompass a broader range of environmental factors, including corrosion resistance and protection against specific hazards. In contrast, IP ratings are internationally recognized and focus specifically on protection against solids and liquids. It’s important to note that while there are equivalency charts between NEMA and IP ratings, they are not directly interchangeable due to these differences.
| NEMA Type | Approximate IP Equivalent | Protection Summary |
|---|---|---|
| NEMA 1 | IP10 | Indoor use; protects against dust and light contact |
| NEMA 3 | IP54 | Outdoor use; protects against rain, sleet, and windblown dust |
| NEMA 4 | IP66 | Indoor/outdoor use; protects against splashing and hose-directed water |
| NEMA 4X | IP66 | Same as NEMA 4 plus corrosion resistance |
| NEMA 6 | IP67 | Protects against temporary submersion |
| NEMA 6P | IP67 | Protects against prolonged submersion |
| NEMA 12 | IP52 | Indoor use; protects against dust and dripping water |
| NEMA 13 | IP54 | Indoor use; protects against dust and spraying of water and non-corrosive coolants |
Note: This table provides approximate equivalents. Always consult specific standards and manufacturer specifications when selecting enclosures.
Key Benefits of Electrical Enclosures
Electrical enclosures aren’t just protective boxes — they’re critical assets that keep operations safe, organized, and efficient across industries. Here’s a closer look at the key benefits, practical examples, and expert tips to help you maximize their value.
1. Equipment Protection: Keeping Systems Running Smoothly
Benefit:
Electrical enclosures shield sensitive components from dust, moisture, debris, extreme temperatures, and physical impacts. By doing so, they extend the lifespan of equipment, minimize downtime, and reduce costly repairs.
Example:
In a food processing plant, stainless steel enclosures protect control panels from high-pressure washdowns and corrosion, ensuring uninterrupted operations.
Pro Tip:
Always match the enclosure material to your environment — for example, use stainless steel in corrosive environments and fiberglass for chemical-heavy settings.
2. Enhanced Electrical Safety: Safeguarding People and Equipment
Benefit:
Enclosures create a barrier between live electrical components and workers, reducing the risk of shocks, fires, and equipment tampering. They also meet safety regulations that protect facilities from legal risks.
Example:
In commercial facilities, NEMA 1 enclosures are often used to safely house indoor electrical wiring and controls, keeping employees and customers safe from accidental contact.
Pro Tip:
Choose enclosures with lockable doors or tamper-proof features if located in high-traffic or public areas to add an extra layer of safety.
3. Organization and Maintenance Efficiency: Streamlining Operations
Benefit:
Well-designed enclosures offer organized spaces for wiring, circuit breakers, and other components. Neat installations make troubleshooting faster, reduce service times, and lower operational costs.
Example:
At manufacturing plants, modular electrical enclosures help maintenance teams quickly locate and repair faults without needing to trace tangled wiring across multiple systems.
Pro Tip:
Opt for enclosures with pre-installed cable management systems or DIN rails to simplify future expansions or modifications.
4. Compliance with Industry Standards: Meeting Regulatory Requirements
Benefit:
Using certified enclosures (NEMA, IP-rated, UL-listed) ensures your systems meet industry safety and operational standards. Compliance can also impact insurance, inspections, and project approvals.
Example:
Utility companies often specify NEMA 4X enclosures for outdoor substations to meet both environmental and safety requirements under OSHA and NEC standards.
Pro Tip:
When bidding for large projects, highlight that your systems use compliant enclosures—this can be a selling point that builds customer trust.

Industry Applications and Use Cases
Electrical enclosures are indispensable across various industries, providing protection, safety, and compliance for electrical systems. Below are detailed applications and use cases across key sectors:
Manufacturing Plants
Use Case: In manufacturing environments, electrical enclosures protect control systems, motor starters, and variable frequency drives from dust, moisture, and mechanical damage.
Example: A metal fabrication plant utilizes NEMA 12 enclosures to safeguard PLCs and HMIs from metal shavings and coolant sprays, ensuring uninterrupted production lines.
Pro Tip: Opt for modular enclosures that allow for scalability and easy integration of additional components as production needs evolve.
Utilities and Power Distribution
Use Case: Electrical enclosures in utilities protect switchgear, transformers, and distribution panels from environmental factors and unauthorized access.
Example: A municipal power distribution center employs NEMA 3R enclosures to house outdoor transformers, providing protection against rain and ice formation.
Pro Tip: Ensure enclosures meet UL and NEMA standards for outdoor use to maintain system reliability and safety.
Oil & Gas Industry
Use Case: In the oil and gas sector, enclosures protect critical control systems from explosive gases, corrosive substances, and extreme temperatures.
Example: An offshore drilling platform uses NEMA 4X stainless steel enclosures with purge systems to house control equipment, preventing ignition of flammable gases.
Pro Tip: Select enclosures certified for hazardous locations (e.g., ATEX, IECEx) to comply with safety regulations and protect personnel.
Food and Beverage Industry
Use Case: Enclosures in this industry must withstand frequent washdowns and prevent contamination, protecting electrical components in hygienic environments.
Example: A dairy processing facility utilizes IP69K-rated stainless steel enclosures with sloped roofs to prevent water accumulation and facilitate cleaning.
Pro Tip: Choose enclosures with hygienic design features, such as smooth surfaces and minimal crevices, to meet food safety standards
Commercial and Residential Projects
Use Case: In commercial and residential settings, enclosures protect electrical panels, circuit breakers, and communication systems from tampering and environmental exposure.
Example: A residential complex installs NEMA 1 enclosures indoors for circuit breaker panels, while using NEMA 3R enclosures outdoors for HVAC controls.
Pro Tip: Ensure enclosures are appropriately rated for their location—indoor or outdoor—and consider aesthetic integration in residential applications.
Selecting the right electrical enclosure tailored to specific industry requirements ensures operational efficiency, safety, and compliance with regulatory standards.
How to Choose the Best Electrical Enclosure for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate electrical enclosure is crucial for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical systems. This section provides a comprehensive checklist and highlights common pitfalls to avoid during the selection process.
Electrical Enclosure Selection Checklist
1. Determine the Installation Environment
- Indoor vs. Outdoor: Indoor environments may require enclosures with basic protection, while outdoor settings demand enclosures resistant to weather elements.
- Hazardous Locations: For areas with explosive gases or dust, select enclosures certified for hazardous locations, such as NEMA Types 7, 8, or 9, or those compliant with IEC 60079 standards.
2. Assess Exposure to Environmental Elements
- Moisture and Dust: Enclosures should have appropriate IP or NEMA ratings to protect against ingress of water and dust.
- Chemicals and Corrosive Substances: In chemical plants or coastal areas, materials like stainless steel or fiberglass offer enhanced corrosion resistance.
3. Evaluate Size and Space Requirements
- Component Accommodation: Ensure the enclosure has sufficient space for all components, including allowances for heat dissipation and future expansions.
- Accessibility: Consider space for maintenance activities and cable management.
4. Verify Compliance and Certifications
- Standards Adherence: Confirm that the enclosure meets relevant standards such as NEMA, IP, UL, or CSA, depending on your regional and industry requirements.
- Industry-Specific Regulations: Certain industries may have additional standards; ensure the enclosure complies accordingly.
5. Choose Appropriate Materials
- Metal Enclosures: Offer durability and are suitable for environments requiring electromagnetic shielding.
- Non-Metallic Enclosures: Materials like polycarbonate or fiberglass are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, ideal for certain outdoor or chemical environments.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Neglecting Thermal Management: Failing to account for heat dissipation can lead to equipment failure. Incorporate ventilation or cooling solutions as needed.
- Overlooking Future Expansion: Selecting an enclosure with no room for additional components can limit scalability. Plan for potential growth.
- Ignoring Environmental Factors: Using enclosures not suited for the specific environmental conditions can result in premature failure.
- Inadequate Sealing: Poor sealing can allow ingress of dust or moisture, compromising the integrity of the enclosure.
- Non-Compliance with Standards: Using enclosures that do not meet required standards can lead to safety hazards and legal issues.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate electrical enclosure is more than a technical decision; it’s a strategic investment in the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical systems. Proper enclosures shield sensitive components from environmental hazards, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
By considering factors such as environmental conditions, material suitability, size requirements, and regulatory compliance, you can choose an enclosure that not only protects your equipment but also enhances operational performance .
Remember, the right enclosure contributes to reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, and improved safety for personnel. It’s an essential component that supports the reliable operation of your electrical infrastructure.
Need Help Selecting the Perfect Electrical Enclosure?
At Electrical Power and Control, we believe choosing the right electrical enclosure shouldn’t be complicated. Our knowledgeable team is here to guide you every step of the way — helping you protect your equipment, meet industry standards, and minimize downtime with solutions tailored to your unique needs.
✅ Whether you’re managing a new installation, upgrading your facility, or tackling a custom project, we offer dependable advice and reliable products you can trust.
👉 Ready to get started? Contact Us today for expert guidance and customized solutions designed to keep your operations running smoothly.