Table of Contents
Toggle
To keep operations running smoothly and safely, industrial and commercial settings need reliable circuit breakers, devices that safeguard electrical systems from overloads and faults. However, when circuit breakers encounter issues, it can lead to costly downtime and equipment failures. This guide will help you identify and solve common circuit breaker problems effectively, so you can prevent disruptions and avoid expensive repairs.
1. Overloading and Tripping Issues
Causes and Symptoms
Overloading and tripping are among the most common circuit breaker issues, especially in industrial and commercial settings where electrical systems operate at high capacity. These problems occur when the current flowing through the circuit exceeds the breaker’s capacity to handle it safely.
Common signs of overloading include:
- Frequent breaker trips: If your circuit breaker trips more often than usual, it may be due to an overloaded system.
- Overheating equipment: Devices connected to the circuit may feel unusually warm or hot to the touch.
- Power interruptions: Sudden power outages in specific areas of the facility can be a sign that a circuit breaker is overwhelmed.
What causes overloading and tripping?
- Excessive electrical loads: When too many high-power devices or machines are connected to the same circuit, the load can surpass the breaker’s rating.
- Faulty wiring or connections: Improper wiring, loose connections, or aging wires can lead to an uneven flow of current, triggering the breaker.
- Underrated breakers: Using a circuit breaker with a capacity lower than the demands of the connected load is a common oversight in industrial settings.
What it Could Cost You
Failing to address overloading and tripping issues can lead to serious financial and operational consequences, such as:
- Project delays: Frequent power interruptions can halt production, leading to missed deadlines and reduced productivity.
- Equipment damage: Persistent overloading can cause overheating, leading to damage or shortened lifespan of expensive equipment.
- Safety hazards: Overheating circuits can pose fire risks, threatening the safety of employees and property.
Solutions
Effectively managing overloading and tripping issues is crucial for maintaining safe and efficient operations. Here are practical steps to address these problems:
- Perform Regular Load Assessments: Conduct periodic checks to evaluate the electrical demand of all equipment connected to the circuit. Identify peak usage times and redistribute loads to prevent overloading a single breaker.
- Ensure Correct Breaker Ratings: Confirm that your circuit breakers are rated appropriately for the equipment they protect. For heavy-duty operations, consider investing in industrial circuit breakers specifically designed to handle higher loads.
- Upgrade Circuit Breakers if Necessary: If your facility has expanded or added new equipment over time, your existing breakers may no longer meet current needs. Upgrade to a higher-capacity breaker or redesign the electrical system to accommodate increased demand.
- Educate Staff: Train employees on proper usage of electrical equipment and the importance of avoiding overloading circuits. Ensure workers understand the warning signs of an overloaded system and how to respond quickly.
- Implement Preventive Maintenance: Schedule regular inspections of your electrical systems to identify potential overloading risks early. Address worn or faulty wiring quickly to avoid unnecessary tripping and interruptions.
By proactively managing load distribution and ensuring your breakers are adequately rated, you can prevent unnecessary downtime and protect your valuable equipment from damage.

2. Aging and Wear
Causes and Symptoms
Over time, circuit breakers experience natural wear and tear due to continuous use, environmental factors, and lack of routine maintenance. This is particularly common in industrial and commercial environments where systems operate under high demand.
Aging components can become less reliable, posing risks to the efficiency and safety of your electrical systems.
Common symptoms of aging and wear include:
- Physical deterioration: Cracks, discoloration, or visible damage on the circuit breaker housing.
- Inconsistent performance: Breakers may trip unpredictably or fail to trip during an overload, indicating internal wear.
- Reduced sensitivity: Older breakers may not respond as quickly to faults, increasing the risk of damage to connected equipment.
- Increased heat: Worn components can cause excessive heat buildup, which may lead to equipment failure or fire hazards.
What causes aging and wear?
- Prolonged usage: Continuous operation without proper maintenance accelerates component degradation.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to moisture, dust, or corrosive substances can speed up wear.
- Outdated technology: Older circuit breakers may not meet modern efficiency and safety standards, making them prone to failure.
What it Could Cost You
Ignoring aging and wear can have significant financial and operational consequences:
- Fire hazards: Deteriorated breakers increase the risk of electrical fires, endangering employees and property.
- Unexpected breakdowns: A failed breaker can halt operations, leading to costly downtime and emergency replacements.
- Higher replacement costs: Replacing damaged systems often costs more than proactive upgrades.
Solutions
To mitigate issues caused by aging and wear:
- Schedule Routine Inspections and Testing: Regularly test breakers to ensure they are operating within safe parameters. Look for signs of wear and address issues before they escalate.
- Replace Aging Components Proactively: Replace outdated or worn circuit breakers before they fail. Consider upgrading to modern industrial circuit breakers that offer enhanced durability and safety features.
- Maintain a Clean Environment: Reduce exposure to harmful environmental factors by keeping electrical rooms clean and well-ventilated.
By proactively addressing aging and wear, you can extend the lifespan of your equipment, improve system reliability, and reduce overall maintenance costs.
3. Loose Connections and Corrosion
Causes and Symptoms
Loose connections and corrosion are common issues that can compromise the reliability and safety of electrical systems. These problems often develop gradually and can go unnoticed until they cause significant disruptions.
Symptoms of loose connections and corrosion include:
- Flickering lights: Inconsistent power flow can cause lights to dim or flicker.
- Increased heat: Loose connections create electrical resistance, generating excess heat that can damage components.
- Visible rust or residue: Corrosion on circuit breaker terminals or contacts is often evident as discoloration, rust, or a powdery buildup.
- Erratic breaker performance: Loose connections may cause the breaker to trip unpredictably or fail to trip during a fault.
What causes loose connections and corrosion?
- Vibrations: Equipment vibrations can gradually loosen screws and terminals over time, especially in industrial settings.
- Environmental exposure: Humidity, water leaks, or exposure to corrosive substances like chemicals can accelerate corrosion.
- Improper installation: Poorly secured connections during installation can lead to early wear and performance issues.
What it Could Cost You
If left unaddressed, loose connections and corrosion can lead to:
- Equipment failures: Poor connectivity disrupts the flow of electricity, damaging machinery and critical systems.
- Safety hazards: Corrosion and heat buildup increase the risk of electrical fires, posing threats to employees and property.
- Expensive repairs: Replacing damaged components or repairing large-scale failures can result in significant downtime and costs.
Solutions
Combat loose connections and corrosion with these effective strategies:
- Conduct Regular Visual Inspections: Periodically check for signs of loose connections or corrosion on terminals, screws, and contacts.
- Apply Anti-Corrosion Treatments: Use protective coatings or sprays designed to prevent rust and oxidation on metal parts.
- Ensure Secure Connections: Tighten screws and terminals during regular maintenance to prevent vibrations from loosening them. Use appropriate tools to avoid overtightening, which can damage components.
By addressing loose connections and corrosion proactively, you can improve system reliability, extend equipment lifespan, and minimize the risks of costly downtime or safety hazards.
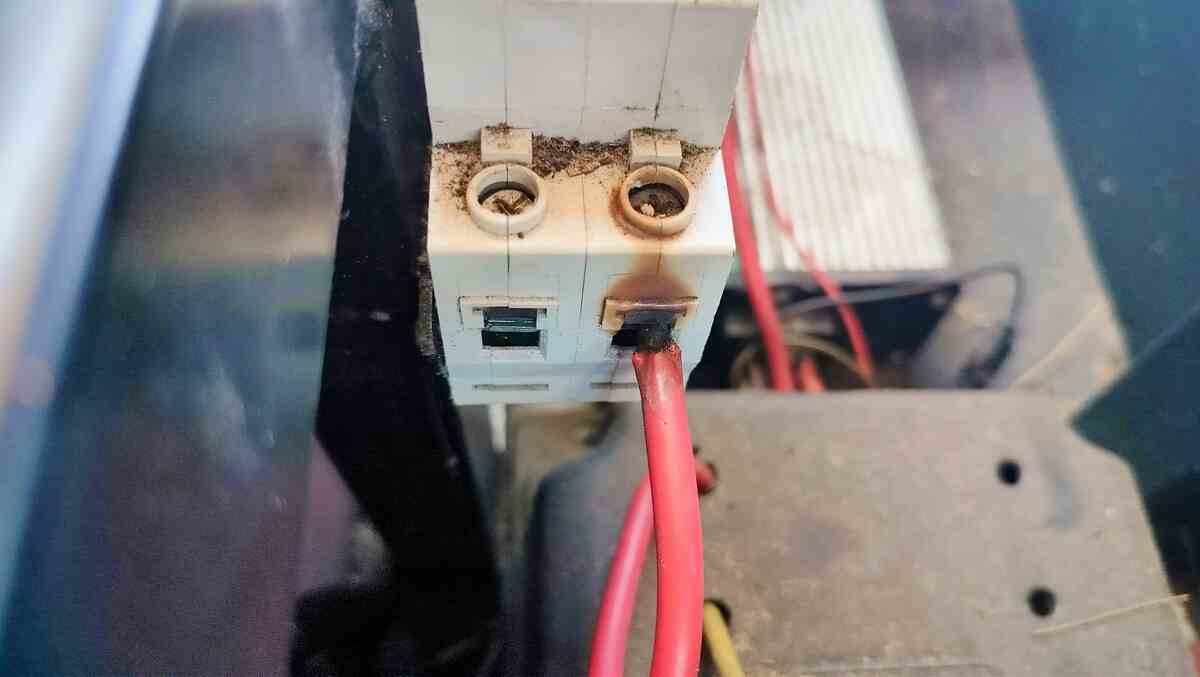

4. Undetected Electrical Faults
Causes and Symptoms
Undetected electrical faults are a hidden danger that can stress your circuit breakers and compromise the performance of your entire electrical system. These faults are particularly problematic in industrial and commercial environments where systems are complex and operate under high loads. They often go unnoticed until they cause significant damage or operational disruptions.
Common symptoms of undetected electrical faults include:
- Unexplained breaker trips: Circuit breakers may trip randomly, even when the load appears to be within limits.
- Reduced equipment performance: Machines connected to the circuit may underperform or exhibit erratic behavior.
- Increased energy consumption: Electrical faults can cause inefficiencies, leading to higher-than-usual energy bills.
- Abnormal sounds or smells: Humming noises or a burning smell near the breaker panel may indicate underlying issues.
What causes undetected electrical faults?
- Worn insulation: Aging or damaged insulation can lead to short circuits or leakage currents.
- Hidden wiring issues: Faulty or improperly installed wiring is a common culprit.
- Component degradation: Internal components of circuit breakers or connected equipment may deteriorate over time, increasing the likelihood of faults.
What it Could Cost You
Leaving electrical faults undetected can lead to severe consequences:
- Escalated repair costs: Minor issues can evolve into major system failures, requiring expensive repairs or replacements.
- Extended downtime: Faults often result in unexpected power outages, halting production and delaying projects.
- System-wide damage: Persistent electrical stress can affect other components, leading to widespread failures and higher maintenance costs.
Solutions
To effectively address undetected electrical faults:
- Utilize Advanced Diagnostic Tools: Invest in thermal imaging, power quality analyzers, and other advanced diagnostic tools to detect faults early. Perform routine testing to monitor system health and identify hidden issues.
- Partner with Experts for Technical Support: Collaborate with experienced electrical service providers to perform comprehensive system evaluations. Ensure you have access to technical expertise for interpreting diagnostic results and implementing solutions.
- Implement Continuous Monitoring: Use real-time monitoring systems to track the performance of your electrical network. Identify anomalies immediately to minimize the risk of damage.
Addressing undetected electrical faults early ensures the safety, reliability, and efficiency of your electrical systems, reducing downtime and preventing costly repairs.
5. Improper Selection and Installation
Causes and Symptoms
Improper selection and installation of circuit breakers can create significant issues in industrial and commercial electrical systems. When the wrong breaker is chosen or installed incorrectly, it can lead to inefficient performance, system vulnerabilities, and even safety hazards.
Signs of improper selection or installation include:
- Inconsistent operation: Circuit breakers may trip without reason or fail to trip during overloads, leaving systems unprotected.
- Frequent failures: Breakers that are incompatible with the system may overheat or wear out prematurely.
- Unstable power distribution: Erratic performance, such as flickering lights or equipment malfunction, may indicate a mismatch in breaker capacity or improper wiring during installation.
What causes these issues?
- Mismatched ratings: Choosing a breaker with a rating that doesn’t align with the system’s load requirements is a common mistake. For example, using a residential-grade breaker in an industrial application can result in inadequate protection.
- Incorrect breaker type: Some systems require specific types of breakers, such as thermal-magnetic, molded case, or ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs). Using the wrong type can compromise safety and performance.
- Improper wiring or mounting: Inadequate installation practices, such as loose connections or improper alignment, can reduce the reliability of the breaker and increase the risk of failure.
What it Could Cost You
Improper selection and installation can lead to several costly problems, including:
- Unnecessary replacements: Breakers that wear out prematurely or are incompatible with the system may need frequent replacement.
- Project delays: Faulty installations can cause downtime, disrupting operations and delaying critical projects.
- Safety risks: Inadequate circuit protection increases the likelihood of electrical fires and equipment damage, leading to significant financial and safety liabilities.
Solutions
To avoid these issues, consider the following best practices:
- Consult with Experts: Partner with knowledgeable suppliers or electrical consultants to select the correct breaker type and rating for your system’s unique requirements. Seek advice on whether upgrades or specialized breakers are needed for new equipment or system expansions.
- Ensure Proper Installation: Make sure you choose a licensed electrician with expertise in industrial and commercial systems to handle breaker installations. Verify that installations adhere to industry standards and local electrical codes.
- Invest in High-Quality Breakers: Use durable, industrial-grade breakers designed to withstand the demands of your system. Avoid attempting to cut costs by purchasing substandard or mismatched equipment.
- Conduct Post-Installation Testing: After installation, perform system tests to confirm proper breaker functionality and compatibility. Regularly inspect installations to ensure connections remain secure and aligned over time.
By selecting the right circuit breaker and ensuring proper installation, you can avoid costly downtime, enhance operational safety, and extend the lifespan of your electrical system components.

Best Practices to Avoid Circuit Breaker Problems
Preventing circuit breaker issues requires a proactive approach, combining regular maintenance, proper equipment selection, and adherence to safety standards. By implementing these best practices, you can reduce downtime, avoid costly repairs, and maintain a safe, reliable electrical system.
1. Implement a Comprehensive Maintenance Schedule
Regular maintenance is essential for identifying and addressing circuit breaker issues before they escalate.
- Routine Inspections: Schedule periodic visual inspections to check for signs of wear, corrosion, loose connections, or physical damage. These inspections help identify potential problems early and prevent unexpected failures.
- Operational Testing: Perform routine tests on circuit breakers to ensure they trip appropriately under fault conditions. This verifies that the breakers are functioning as intended and providing adequate protection.
- Clean and Lubricate Components: Dust, dirt, and debris can accumulate on breaker components, leading to poor performance. Regular cleaning and lubrication improve reliability and prevent malfunctioning.
2. Select the Right Circuit Breaker
Using the correct circuit breaker for your system’s requirements is critical.
- Match Ratings to System Needs: Look at the breaker’s catalog number and ensure the breaker’s voltage, current, and interrupting ratings align with your electrical load. Underrated breakers may trip unnecessarily, while overrated breakers may fail to provide adequate protection.
- Choose Breaker Types Based on Application: Different environments require different types of breakers (e.g., thermal-magnetic, GFCIs, or air circuit breakers). Consult with an expert to select the right type for your application.
3. Train Your Team on Proper Usage
Educate your staff on how to operate electrical systems safely and detect early signs of circuit breaker issues.
- Awareness of Warning Signs: Train employees to recognize flickering lights, frequent tripping, and overheating, which may signal potential problems.
- Safe Equipment Use: Ensure workers understand load limits and avoid connecting excessive devices to a single circuit.
4. Conduct Regular System Assessments
Periodic system evaluations can uncover hidden faults and inefficiencies.
- Load Analysis: Perform load assessments to identify circuits nearing capacity and redistribute loads to prevent overloading.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Use modern diagnostic tools, such as infrared thermography or power quality analyzers, to detect hidden electrical faults that may stress circuit breakers and other components.
5. Partner with Trusted Suppliers and Experts
Collaborate with reliable suppliers and professionals who specialize in electrical systems.
- Supplier Support: Partner with suppliers who offer high-quality, industrial-grade circuit breakers designed for durability and performance.
- Expert Maintenance Services: Engage certified technicians or consultants for advanced troubleshooting, repairs, and installations.
6. Follow Installation Best Practices
Proper installation reduces the risk of future circuit breaker problems.
- Certified Electricians Only: Always hire licensed professionals to install or replace circuit breakers.
- Adhere to Standards and Codes: Ensure installations meet all local and industry electrical codes to maintain safety and efficiency.
7. Monitor Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors, such as heat, humidity, and dust, can affect circuit breaker performance.
- Control Temperature and Humidity: Ensure breaker enclosures are in well-ventilated, climate-controlled areas to prevent overheating and corrosion.
- Protect Against Dust and Debris: Use sealed enclosures or covers to shield circuit breakers from contaminants in harsh industrial environments.
By implementing these best practices, you can maintain the efficiency and safety of your electrical systems while avoiding unexpected disruptions.
Conclusion
Addressing circuit breaker issues promptly can prevent downtime, reduce repair costs, and keep your systems running efficiently. By following the practical tips in this guide, you can avoid common problems and maintain reliable operations.
Need expert help or reliable circuit breaker solutions? Contact us at (205) 812-5402. We’re here to support you with dependable products and professional advice tailored to your needs.