Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Control Components of the Masterpact Square D NW Breaker
The Masterpact Square D NW circuit breaker is a crucial electrical device used in various electrical applications. Understanding its control components is essential for safe and efficient operation.
To delve deeper into its functionality, we’ll explore the control circuit options and associated identification codes. In this article, we’ll break down these codes, share a fun fact about the breaker, and emphasize the importance of matching control components with the correct voltage for your system.
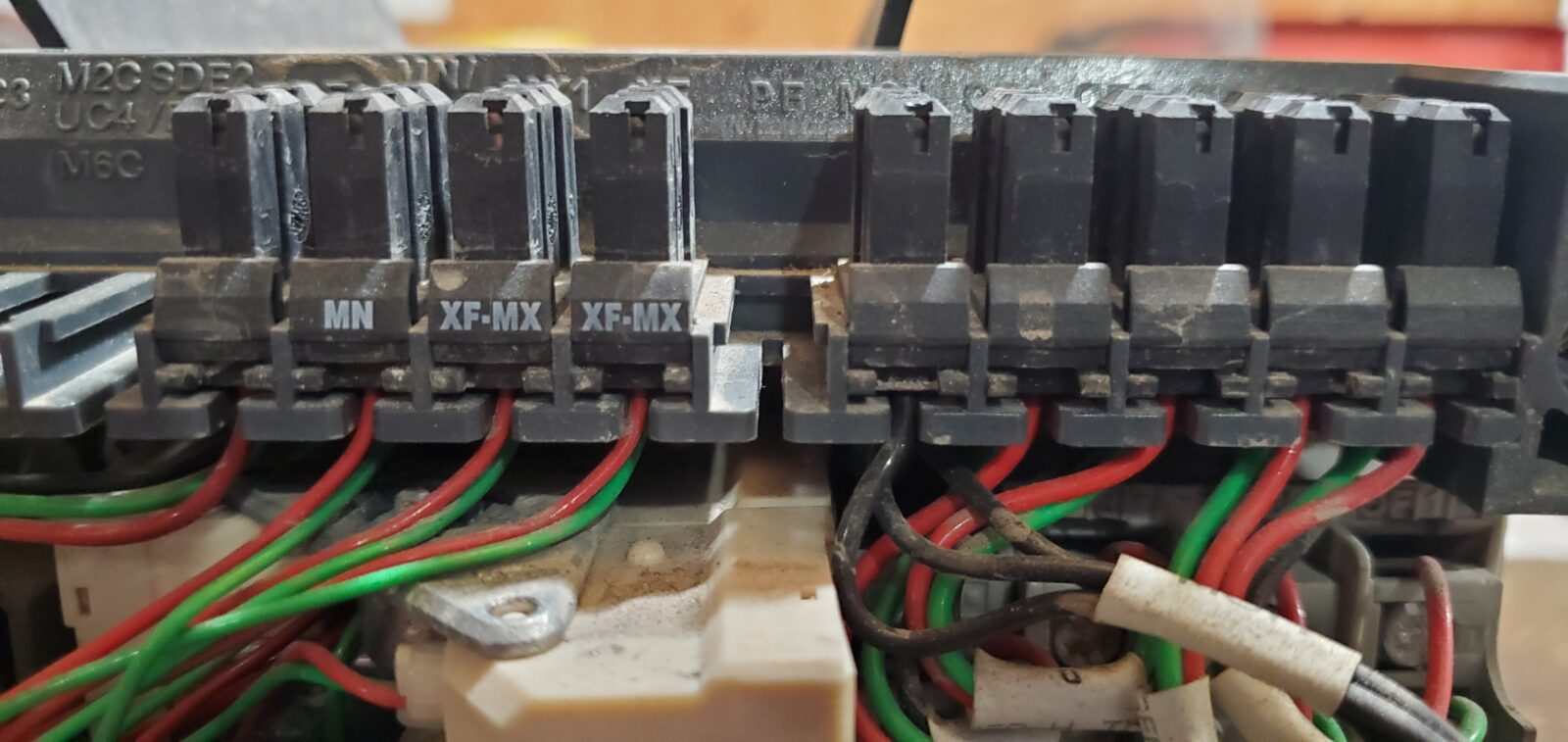
Cracking the Masterpact NW Breaker Code
To better understand the Masterpact NW breaker, let’s decipher the identification codes for its control components:
1. MX – Shunt Trip: The MX code represents the shunt trip function. This component plays a role in opening the breaker when needed, typically triggered by an overload, short circuit, or external control signal.
2. XF – Shunt Close: The XF code stands for shunt close. Unlike the shunt trip, this component helps close the circuit breaker. The shunt close provides the extra closing force needed to overcome friction in the breaker mechanism, which can increase over time due to wear and tear, and manage the initial surge in current, ensuring a secure and reliable closure.
3. MN – U.V. Under Voltage Coil: The MN code corresponds to the undervoltage coil, which monitors and responds to voltage changes. If the system voltage falls below a predetermined threshold, the undervoltage coil trips the breaker open, protecting equipment from damage caused by low voltage conditions.
4. MCH – Charging Motor: MCH denotes the charging motor, an essential part of the breaker’s operation. It is responsible for compressing the spring within the closing mechanism. This stored energy is then released when the breaker needs to close.
A Fun Fact
Here’s a surprising fact about the Masterpact NW circuit breaker: the shunt trip (MX code) and shunt close (XF code) coils, although seemingly opposite in function, share a surprising secret – they’re actually interchangeable parts! This might seem counterintuitive, but the key lies in their placement within the breaker mechanism.
Think of these coils like tiny electromagnets. When energized, they create a magnetic field that interacts with the circuit breaker’s internal mechanics. However, the location where you install the coil determines its specific role.
- Shunt Trip (MX): Mounted in a specific location, the MX coil engages a mechanism designed to trip (open) the breaker contacts. When energized, the magnetic field from the coil pulls on a designated latch, releasing the spring-loaded closing mechanism and forcing the breaker contacts apart.
- Shunt Close (XF): By flipping the script and installing the same coil (MX) in a different location within the breaker, it engages a separate mechanism designed for closing. In this scenario, the magnetic field from the energized coil interacts with a different latch, releasing the stored energy from the charged spring mechanism. This surge of energy drives the breaker contacts together, effectively closing the circuit.
It’s like having a single key that can unlock two different doors depending on where you insert it. In the NW breaker, the interchangeable coil acts as the “key,” while its placement determines whether it unlocks the “trip” or “close” function. This clever design offers some flexibility during maintenance or troubleshooting. A qualified electrician can swap the coil’s location to convert it from a trip to a close function (or vice versa) if necessary.
A Word of Caution
The world of electrical components may seem complex, but a single misstep can have serious consequences. When dealing with control components for the Masterpact NW breaker, voltage matching is paramount. Here’s why:
- Safety First: Control components are designed for specific voltage ratings. Using a mismatched voltage coil can lead to malfunctions that compromise safety. For example, a low-voltage coil designed for a 208V system wouldn’t generate enough magnetic force in a 480V system.
- Ensuring Reliable Operation: Each voltage rating corresponds to specific operational characteristics. A mismatched coil wouldn’t function as intended, potentially causing the circuit breaker to trip or fail to close at the correct time. This could disrupt critical processes or even damage connected equipment.
- Identifying Voltage Requirements: Fortunately, determining the correct voltage is straightforward. The voltage rating is typically printed directly on the plastic label of the control component you’re replacing. Additionally, the NW circuit breaker’s technical specifications or user manual will also list compatible voltage ratings for its control components.
Understanding the control components and identification codes of the Masterpact Square D NW breaker is vital for its proper operation.
By learning about these control components their interchangeability, and adhering to voltage requirements, you can ensure this essential electrical device’s efficient and safe functioning. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting in the field, this knowledge will help you harness the full potential of the NW circuit breaker in your applications.
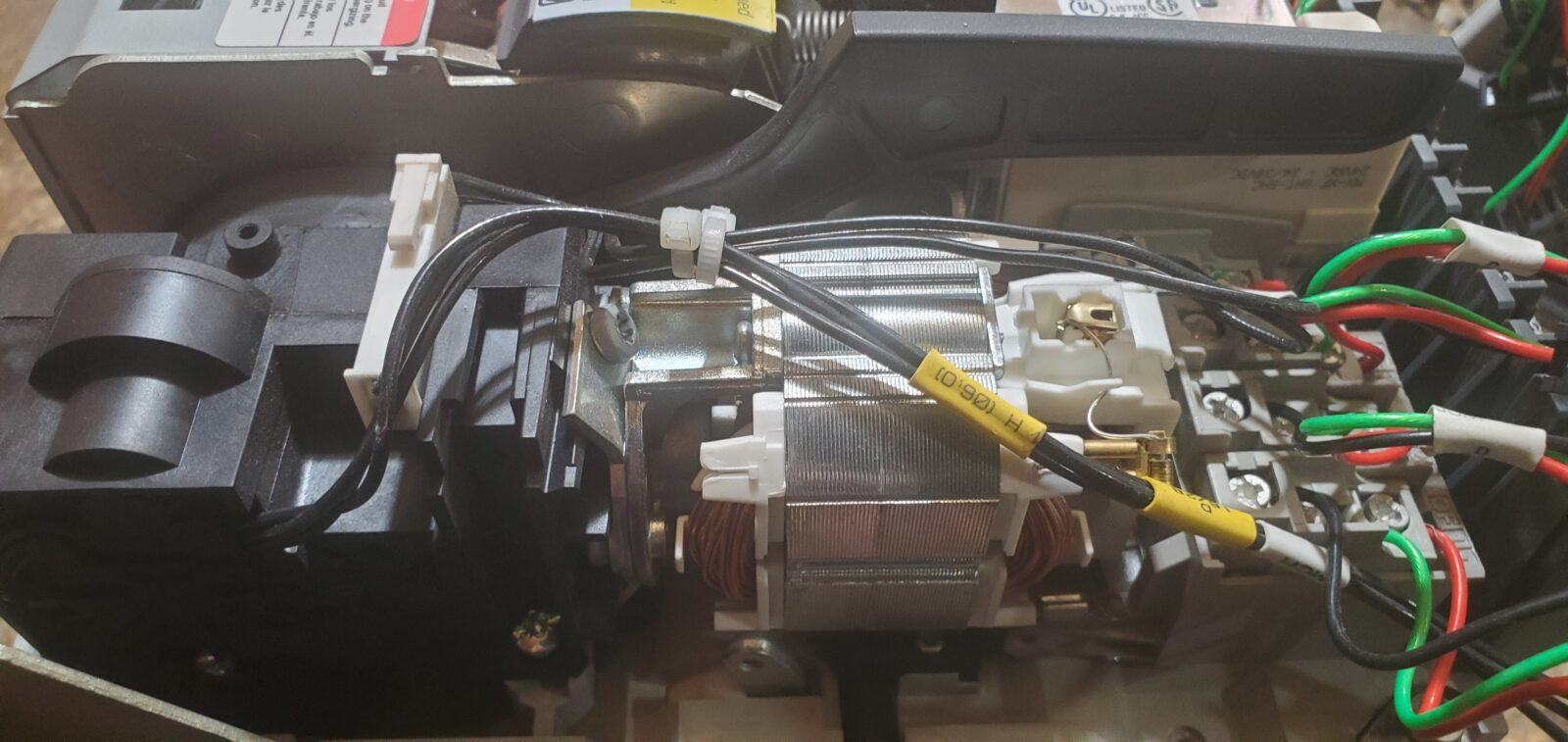

Understanding the control components of your Masterpact NW circuit breaker is a valuable first step… But if you’re looking to get hands-on and replace a worn-out MCH (charging motor), we’ve got you covered!
Our video takes you through the process step-by-step, showing you how to remove casings and detach the old motor, as well as how to put the new one in correctly and test that it’s working properly. See you there!
