Table of Contents
Toggle- What Are Industrial Circuit Breakers?
- Why Are They Important?
- Types of Industrial Circuit Breakers
- How to Choose the Right Circuit Breaker for Your Industrial Needs
- Maintenance of Industrial Circuit Breakers: Preventing Failures and Ensuring Longevity
- Real-World Applications of Industrial Circuit Breakers
- Conclusion: Choosing the Right Circuit Breaker for a Safer, More Efficient Operation
- Take Action: Protect Your Business from Costly Downtime and Electrical Failures!
Imagine you’re running a manufacturing facility, and everything is operating smoothly—until suddenly, the power cuts out.
A vital piece of equipment shuts down, production grinds to a halt, and every second of downtime is costing your business money. The culprit? A circuit overload that could have been prevented with the right industrial circuit breaker.
Circuit breakers are the silent protectors of electrical systems. They shield your equipment, workers, and entire operations from dangerous overloads and short circuits.
But not all circuit breakers are created equal—each type is designed for specific applications and industries.
If you’ve ever felt overwhelmed by the technical jargon surrounding circuit breakers, don’t worry. This guide will walk you through the different types of industrial circuit breakers, how they work, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Whether you manage a factory, oversee facility maintenance, or work as an electrical contractor, understanding circuit breakers is essential to keeping your business running safely and efficiently.
What Are Industrial Circuit Breakers?
If you’ve ever wondered what keeps industrial electrical systems from spiraling into chaos during a fault, the answer lies in circuit breakers. These essential components act as automated sentinels, standing guard against electrical overloads, short circuits, and other potentially catastrophic failures.
At their core, industrial circuit breakers are designed to protect electrical equipment and prevent fires or severe damage caused by excessive current flow. When an abnormality occurs—whether it’s a surge, a fault, or an overload—the breaker detects the issue and automatically shuts off the electrical supply before things get out of hand.
Unlike residential circuit breakers, which you might find in your home’s electrical panel, industrial circuit breakers are built for high-demand environments such as manufacturing plants, commercial buildings, and power stations. They are designed to handle higher voltages, heavier loads, and more complex operational needs.
Why Are They Important?
Without industrial circuit breakers, electrical faults could lead to:
- Costly downtime due to damaged machinery.
- Dangerous electrical fires.
- Compliance violations with OSHA, NEC, and other safety standards.
- Permanent damage to expensive industrial equipment.
Now that you have a basic understanding of why industrial circuit breakers matter, let’s explore the different types and how each one plays a unique role in keeping industrial operations safe and efficient.
Types of Industrial Circuit Breakers
When it comes to industrial electrical systems, not all circuit breakers are created equal. Each type serves a unique purpose, providing protection in different scenarios. Some are built for high voltage power distribution, while others focus on preventing electrical shocks or safeguarding expensive machinery.
Let’s dive deeper into the most commonly used industrial circuit breakers, how they work, their components, and where they are best utilized.
Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCB) – Heavy-Duty Protection for High Current Loads
How Do MCCBs Work?
MCCBs are designed to protect electrical circuits from overload and short circuits by using thermal and magnetic trip mechanisms:
- Thermal Protection: A bimetallic strip heats up when excessive current flows through it. If the overcurrent persists, the strip bends and trips the breaker, cutting off power.
- Magnetic Protection: If a short circuit occurs, a magnetic coil instantly creates a strong magnetic field that trips the breaker immediately, preventing catastrophic damage.
Key Components of MCCBs
- Molded Insulated Case: Provides structural support and protects internal components.
- Bimetallic Strip: Warps when exposed to excessive heat, triggering an overload trip.
- Electromagnet: Detects short circuits and immediately trips the breaker.
- Contacts: Conduct electrical current during normal operations and open during faults.
- Arc Chute: Extinguishes the electrical arc that forms when the breaker trips.
Why Choose an MCCB?
- Handles high currents (100A – 2500A)
- Adjustable trip settings for customized protection
- Robust and durable – ideal for demanding environments
Air Circuit Breakers (ACB) – Best for High Voltage Power Distribution
How Do ACBs Work?
ACBs are used in high-voltage applications and operate using air as the arc-quenching medium. When a fault occurs:
- The contacts separate, creating an electrical arc.
- The arc is cooled and stretched using an arc chute.
- The breaker safely interrupts the fault, protecting the system.
Key Components of ACBs
- Main Contacts – Conduct electricity under normal conditions.
- Arcing Contacts – Handle arc formation before main contacts separate.
- Arc Chute – A structure that absorbs and cools the arc.
- Trip Unit – Monitors electrical conditions and triggers tripping when needed.
Why Choose an ACB?
- Ideal for handling high fault currents
- Enhanced safety due to air-based arc extinguishing
- Remote operation capability for automation
Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCB) – Life-Saving Protection Against Electric Shock
How Do RCCBs Work?
Unlike MCCBs and ACBs, which protect equipment, RCCBs focus on protecting people from electric shocks.
- RCCBs constantly monitor the current balance between the live and neutral wires.
- If there’s an imbalance (indicating a leakage, potentially through a person), the RCCB instantly trips the circuit to prevent electrocution.
Key Components of RCCBs
- Core-Balanced Transformer – Detects imbalances in the electrical current.
- Trip Mechanism – Activates when a leakage current is detected.
- Test Button – Allows manual testing of the RCCB’s function.
Why Choose an RCCB?
- Prevents fatal electric shocks
- Complies with workplace electrical safety standards
- Fast response time – typically within milliseconds
High Voltage Circuit Breakers (HVCB) – Protecting Power Grids
How Do HVCBs Work?
HVCBs are designed for extra-high voltages (above 72kV). They interrupt fault currents using various arc-extinguishing mediums, including:
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCB) – Use a vacuum to quench the arc.
- SF6 Gas Circuit Breakers – Use sulfur hexafluoride gas for arc suppression.
- Oil Circuit Breakers (OCB) – Use insulating oil to cool and quench the arc.
Key Components of HVCBs
- Interrupting Chamber – Houses the arc-extinguishing medium.
- Operating Mechanism – Controls breaker operation (manual or automatic).
- Insulation System – Ensures electrical isolation of high-voltage components.
Why Choose an HVCB?
- Essential for high-voltage infrastructure
- Multiple types available for different applications
- Prevents massive power failures in transmission networks
Motor Protection Circuit Breakers (MPCB) – Safeguarding Industrial Motors
How Do MPCBs Work?
MPCBs are specialized circuit breakers designed to protect motors from overload, phase failures, and short circuits.
- They monitor the motor’s electrical current and trip when irregularities occur.
- Unlike standard circuit breakers, MPCBs offer phase-loss protection to prevent motor burnout.
Key Components of MPCBs
- Overload Relay – Detects overheating conditions.
- Phase-Loss Protection – Ensures all three phases are functioning.
- Short Circuit Protection – Trips instantly when a short circuit occurs.
Why Choose an MPCB?
- Extends motor lifespan by preventing electrical damage
- Prevents costly equipment failures
- Optimized for motor protection
Comparison Table of Industrial Circuit Breakers
| Circuit Breaker Type | Best Used For | Voltage Range | Protection Type | Example Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCCB | Industrial machinery | Low to medium (100A – 2500A) | Overload & short circuit | Manufacturing plants |
| ACB | Power distribution | High (1000A and above) | Overcurrent & short circuit | Electrical substations |
| RCCB | Personal safety | Low (10mA – 300mA sensitivity) | Earth leakage protection | Industrial control panels |
| HVCB | Power grids | Very high (72kV and above) | Arc fault protection | Wind farms |
| MPCB | Electric motors | Low (motor-specific) | Motor overload & phase loss | HVAC systems |
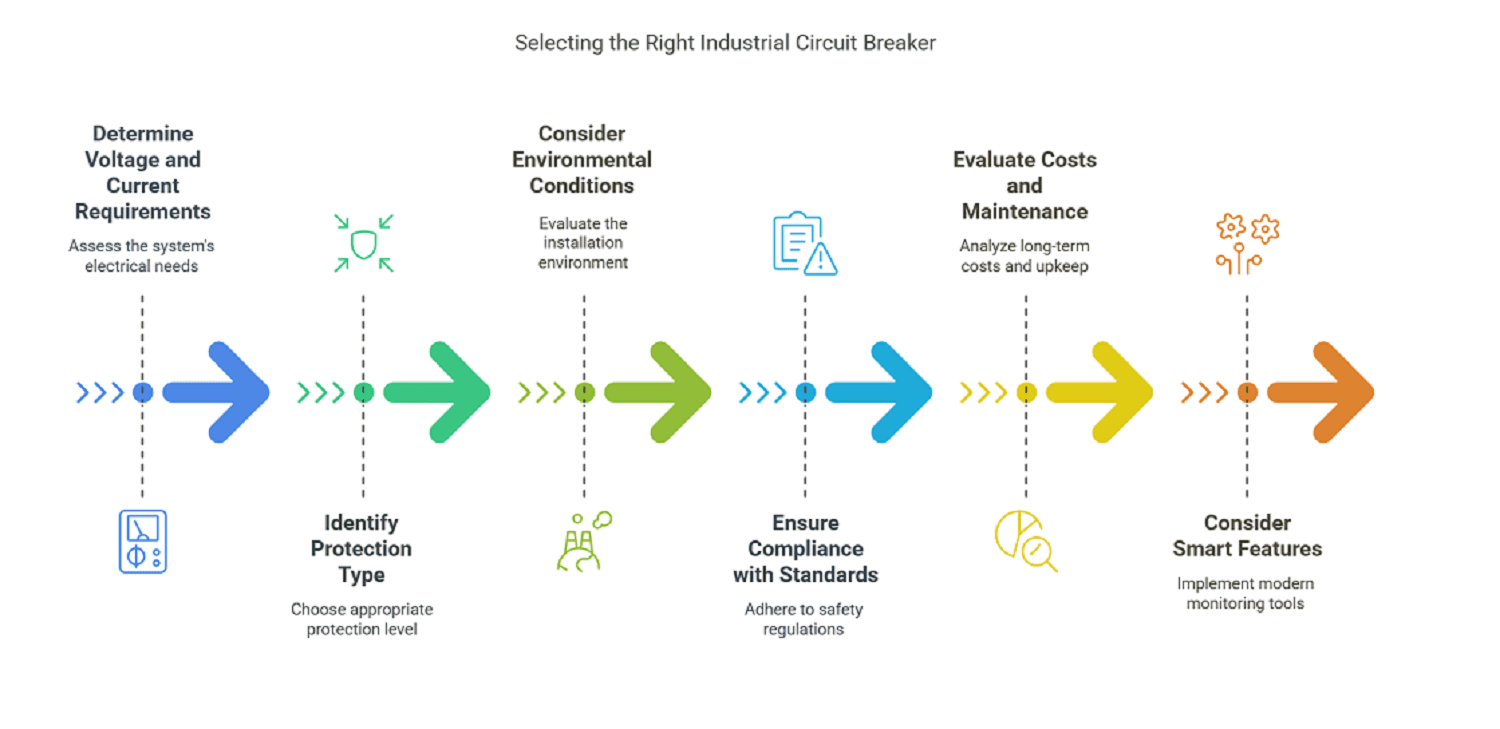
How to Choose the Right Circuit Breaker for Your Industrial Needs
Selecting the right industrial circuit breaker isn’t just about picking one that fits. It’s about ensuring the safety, efficiency, and reliability of your electrical systems. The wrong choice could mean frequent downtime, costly equipment damage, or even safety hazards.
So, how do you choose the perfect circuit breaker for your facility or project? Let’s break it down step by step.
Step 1: Determine Your System’s Voltage and Current Requirements
The first and most crucial factor is understanding how much voltage and current your electrical system operates on. Circuit breakers come in different voltage and current ratings, and choosing the wrong one can lead to system failures.
- Low Voltage Applications (Up to 1000V): MCCBs, RCCBs, and MPCBs are typically used.
- Medium to High Voltage Applications (Above 1000V): ACBs and HVCBs are required.
Example:
If you’re running a large industrial motor, you might need an MCCB with a current rating of 400A or more. However, if you’re protecting an entire substation, an HVCB would be necessary.
Step 2: Identify the Type of Protection Required
Different circuit breakers offer different levels of protection. Ask yourself: What am I trying to protect?
- Overload & Short Circuit Protection → MCCB, ACB, MPCB
- High Voltage Fault Protection → HVCB
- Personal Safety & Shock Protection → RCCB
Example:
In a food processing plant, where water exposure is high, RCCBs are crucial for preventing electric shocks. However, for protecting conveyor belts and machinery, an MCCB or MPCB would be more appropriate.
Step 3: Consider Environmental Conditions
The environment where your breaker will be installed affects performance and longevity.
- High dust, humidity, or corrosive environments → Choose sealed or gas-insulated breakers (HVCBs, MCCBs in enclosed panels).
- Frequent switching requirements → ACBs and MCCBs are more durable for regular operations.
- Outdoor Installations → HVCBs are designed for power grids and external setups.
Example:
An HVCB in a solar power plant substation needs to withstand extreme weather conditions, so a gas-insulated breaker would be ideal.
Step 4: Ensure Compliance with Industry Standards
For businesses in the U.S., industrial circuit breakers must comply with safety regulations such as:
- NEC (National Electrical Code) – Defines circuit breaker ratings and applications.
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) – Ensures workplace safety standards.
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories) Listings – Verifies the safety of electrical components.
Failing to adhere to these regulations can lead to hefty fines, liability risks, and unsafe working conditions.
Step 5: Evaluate Long-Term Costs and Maintenance Needs
- MCCBs and MPCBs require minimal maintenance but may need occasional testing.
- HVCBs and ACBs need periodic inspections due to high-voltage operations.
- RCCBs should be tested regularly to ensure functionality (test button available).
Example:
A manufacturing plant operating 24/7 needs circuit breakers that can handle high loads without frequent maintenance—making MCCBs and ACBs an ideal choice.
Step 6: Consider Smart Features and Remote Monitoring
With the rise of smart electrical systems, modern industrial circuit breakers offer:
- Remote operation and monitoring (useful for ACBs and HVCBs).
- Predictive maintenance alerts to prevent unexpected failures.
- Energy efficiency tracking to reduce power consumption.
Example:
A data center uses smart ACBs with remote monitoring, allowing technicians to detect potential failures before they happen, reducing the risk of downtime.
Final Checklist: Choosing Your Circuit Breaker
| Factor | MCCB | ACB | RCCB | HVCB | MPCB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage Level | Low to Medium | Medium to High | Low | High | Low |
| Best for | Machinery, power distribution | Industrial panels, generators | Personal safety | Power grids, substations | Motor protection |
| Main Protection | Overload & short circuit | High voltage fault protection | Electric shock prevention | Arc faults & power surges | Motor overload & phase failure |
| Where to Use | Factories, plants, commercial buildings | Electrical substations, power panels | Industrial control rooms, wet environments | Wind farms, solar stations | Conveyor belts, pumps, HVAC |
Key Takeaways
- For large industrial equipment: MCCBs and ACBs are best.
- For high-voltage applications: HVCBs are the right choice.
- For personal safety and shock prevention: RCCBs are essential.
- For motor-driven applications: MPCBs are specifically designed for motors.
By selecting the right industrial circuit breaker, you’re not just protecting your equipment—you’re ensuring operational efficiency, reducing downtime, and keeping your workplace safe.
Maintenance of Industrial Circuit Breakers: Preventing Failures and Ensuring Longevity
Industrial circuit breakers are the unsung heroes of electrical systems, tirelessly protecting equipment and personnel from electrical faults. However, like all mechanical devices, they require regular maintenance to function optimally. Neglecting this can lead to unexpected failures, costly downtime, and safety hazards. This section delves into the common causes of circuit breaker failures, essential maintenance practices, and precautions to ensure their reliable operation.
Common Causes of Circuit Breaker Failures
- Overloading and Tripping Issues
- Causes: Connecting too many high-power devices to a single circuit can exceed the breaker’s capacity, leading to frequent trips. Faulty wiring or undersized breakers can exacerbate this issue.
- Symptoms: Frequent breaker trips, overheating equipment, and unexpected power outages in specific areas.
- Aging and Wear
- Causes: Continuous operation, exposure to harsh environmental conditions, and lack of routine maintenance can degrade breaker components over time.
- Symptoms: Physical deterioration like cracks or discoloration, inconsistent performance, reduced sensitivity to faults, and increased heat generation.
- Loose Connections and Corrosion
- Causes: Vibrations from machinery, environmental factors like humidity or exposure to corrosive substances, and improper installation can lead to loose connections and corrosion.
- Symptoms: Flickering lights, excessive heat, visible rust or residue on components, and erratic breaker performance.
- Undetected Electrical Faults
- Causes: Hidden issues such as insulation degradation, moisture ingress, or minor faults that haven’t yet caused a complete failure.
- Symptoms: Unexplained breaker trips, intermittent equipment malfunctions, and signs of overheating without an apparent cause.
Preventive Maintenance Practices
- Regular Visual and Mechanical Inspections
- Procedure: Conduct routine checks for signs of wear, overheating, or physical damage. Ensure all connections are tight and free from corrosion.
- Frequency: Monthly visual inspections; mechanical inspections at least annually.
- Testing and Calibration
- Procedure: Perform electrical tests such as insulation resistance, contact resistance, and operational timing tests. Calibrate protection relays and trip settings to ensure accurate operation.
- Frequency: Annually or as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Cleaning and Lubrication
- Procedure: Clean components to remove dust and debris using appropriate methods. Lubricate moving parts to prevent mechanical wear.
- Frequency: Semi-annually or based on environmental conditions.
- Environmental Control
- Procedure: Maintain a clean, dry, and temperature-controlled environment to prevent moisture ingress and corrosion.
- Frequency: Continuous monitoring with periodic assessments.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping
- Procedure: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, tests performed, and any issues detected.
- Frequency: Update records after every maintenance activity.
Precautions to Prevent Failures
- Proper Installation: Ensure that circuit breakers are installed according to manufacturer specifications and industry standards to prevent operational issues.
- Load Management: Avoid overloading circuits by distributing electrical loads appropriately and upgrading breakers as needed to handle increased demand.
- Training and Awareness: Educate personnel on the importance of regular maintenance, recognizing early signs of breaker issues, and safe operation practices.
- Use of Protective Equipment: Always employ appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) during maintenance to safeguard against electrical hazards.
By adhering to these maintenance practices and precautions, you can enhance the reliability, safety, and lifespan of your industrial circuit breakers, ensuring uninterrupted operation of your electrical systems.
Real-World Applications of Industrial Circuit Breakers
Industrial circuit breakers are not just theoretical components—they play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems across various industries. From manufacturing plants to data centers, these circuit breakers prevent catastrophic failures, protect personnel, and minimize downtime.
Let’s explore real-world scenarios where different types of circuit breakers are essential.
Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB) – Protecting Heavy Machinery in Manufacturing Plants
Application:
A large automotive manufacturing plant relies on conveyor belts and robotic arms for assembling car components. These machines operate on high current loads, and any power surges or faults can disrupt the entire assembly line.
How MCCBs Help:
- Overload Protection: Prevents overheating of motors and electrical systems.
- Short Circuit Prevention: Detects sudden current spikes and instantly disconnects power to prevent damage.
- Adjustable Trip Settings: Ensures the breaker matches the plant’s specific operational needs.
Example Scenario:
A motor-driven conveyor belt suddenly draws excessive current due to mechanical blockage. The MCCB detects the anomaly and trips the circuit before the motor overheats, preventing fire hazards and costly repairs.
Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) – Safeguarding Power Distribution in Data Centers
Application:
A large-scale data center houses thousands of servers that require a continuous and stable power supply. Even a minor electrical fault can lead to data loss, downtime, and financial losses.
How ACBs Help:
- Handles High Fault Currents: Protects the main power distribution panels from sudden power surges.
- Remote Monitoring & Operation: Allows operators to diagnose and reset the breaker remotely.
- Seamless Backup Power Integration: Ensures smooth switching between mains power and backup generators.
Example Scenario:
A power fluctuation occurs due to an unstable power grid. The ACB detects the voltage irregularity and immediately switches to backup generators, ensuring uninterrupted operation of the data center without downtime.
Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) – Ensuring Safety in Construction Sites
Application:
A high-rise building construction site involves workers using electric drills, welding machines, and temporary power setups. Wet conditions and exposed wiring increase the risk of electric shocks.
How RCCBs Help:
- Shock Protection: Instantly trips the circuit when leakage current is detected.
- Prevents Electrical Fires: Detects faulty insulation before it causes a fire.
- Ensures Compliance with Safety Regulations: Meets OSHA standards for worker protection.
Example Scenario:
A worker accidentally touches an exposed wire while handling metal scaffolding. The RCCB detects the leakage current flowing through the worker’s body and instantly cuts off power, preventing a fatal electric shock.
High Voltage Circuit Breaker (HVCB) – Protecting Electrical Substations & Power Grids
Application:
A wind farm substation transmits power from wind turbines to the main power grid. These substations handle extremely high voltages (above 72kV), making them vulnerable to electrical faults caused by lightning strikes or switching surges.
How HVCBs Help:
- Prevents Grid Failures: Quickly isolates faults to avoid widespread blackouts.
- Handles Extreme Voltages: Designed to break high-voltage circuits safely.
- Long Operational Life: Requires minimal maintenance for stable grid performance.
Example Scenario:
During a thunderstorm, a lightning strike causes a power surge in the transmission line. The HVCB detects the excess voltage and trips within milliseconds, preventing damage to transformers and ensuring continued power supply to nearby cities.
Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB) – Enhancing Pump Performance in Water Treatment Plants
Application:
A municipal water treatment facility relies on industrial pumps to transport water through filtration and distribution systems. These pumps operate continuously, making them prone to overloading and phase imbalances.
How MPCBs Help:
- Protects Motors from Overload: Prevents overheating and burnout.
- Phase Failure Detection: Trips if one of the three-phase power supplies fails.
- Increases Pump Lifespan: Reduces mechanical stress on motors.
Example Scenario:
A pump in the treatment facility starts drawing excessive current due to sediment blockage. The MPCB detects the overload and immediately shuts off the motor, preventing damage and allowing maintenance teams to clear the blockage before restarting operations.
| Industry | Circuit Breaker Used | Why It’s Needed | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | MCCB | Prevents machinery overload and fire hazards | Protecting conveyor belts in an automotive factory |
| Data Centers | ACB | Ensures uninterrupted power supply | Switching between main power and generators |
| Construction Sites | RCCB | Prevents electric shocks and meets safety standards | Protecting workers using power tools |
| Power Grids & Substations | HVCB | Isolates high-voltage faults to prevent blackouts | Protecting wind farm substations from surges |
| Water Treatment Plants | MPCB | Prevents motor burnout and extends lifespan | Protecting industrial pumps from phase failure |
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Circuit Breaker for a Safer, More Efficient Operation
Industrial circuit breakers are more than just electrical components—they are the first line of defense against power failures, electrical fires, equipment damage, and even life-threatening shocks. Whether you are managing a manufacturing plant, data center, power grid, or construction site, selecting the right breaker ensures safety, efficiency, and uninterrupted operations.
Key Takeaways
- MCCBs are best for protecting heavy machinery and industrial electrical systems from overload and short circuits.
- ACBs are ideal for large-scale power distribution, ensuring reliable switching between mains and backup power.
- RCCBs are essential for human safety, cutting off power immediately when leakage currents are detected.
- HVCBs play a critical role in power grids and substations, handling high voltages and preventing massive failures.
- MPCBs are specifically designed for motor protection, preventing phase failures and overloads in industrial equipment.
By investing in the right circuit breaker and maintaining it properly, businesses can avoid costly downtime, ensure compliance with safety regulations, and extend the lifespan of their electrical systems.
Take Action: Protect Your Business from Costly Downtime and Electrical Failures!
Every second of downtime costs money. Every electrical failure puts your equipment—and your people—at risk. You’ve worked too hard to let preventable issues disrupt your operations.
At Electrical Power and Control, we don’t just sell circuit breakers—we provide peace of mind. Our experts understand the challenges you face, and we’re here to help you find the perfect protection for your facility, ensuring safety, reliability, and efficiency.
🔧 Need guidance on choosing the right circuit breaker? We’ll walk you through the best options tailored to your needs.
⚡ Looking for fast, reliable delivery? We make sure you get the protection you need—when you need it.
💡 Want to prevent costly electrical failures? We’ll help you build a system that keeps your operations running smoothly.
Don’t wait for a failure to remind you of what’s at stake. Let’s secure your electrical system today.
👉 Talk to Our Experts Now and take control of your power!